OOB Errors for Random Forests¶
The RandomForestClassifier is trained using bootstrap aggregation, where
each new tree is fit from a bootstrap sample of the training observations
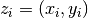 . The out-of-bag (OOB) error is the average error for
each
. The out-of-bag (OOB) error is the average error for
each 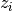 calculated using predictions from the trees that do not
contain
calculated using predictions from the trees that do not
contain 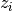 in their respective bootstrap sample. This allows the
in their respective bootstrap sample. This allows the
RandomForestClassifier to be fit and validated whilst being trained [1].
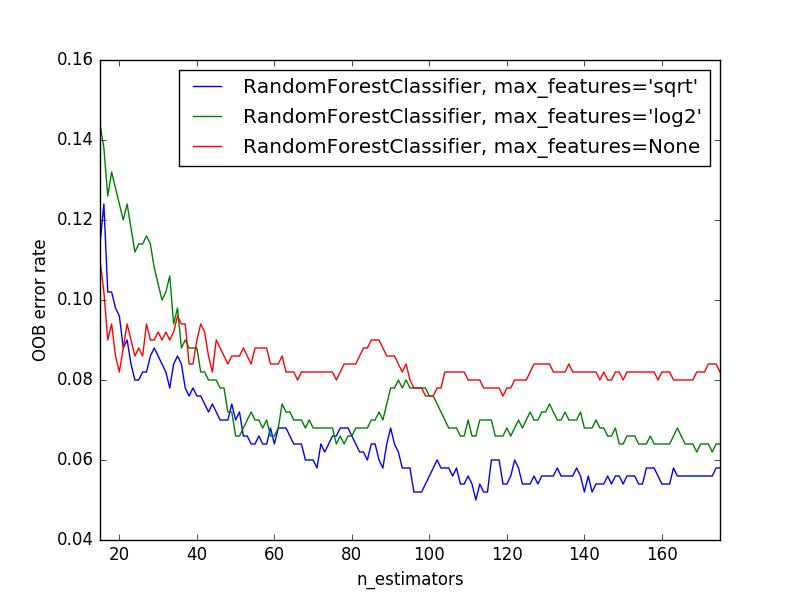
The example below demonstrates how the OOB error can be measured at the
addition of each new tree during training. The resulting plot allows a
practitioner to approximate a suitable value of n_estimators at which the
error stabilizes.
| [1] | T. Hastie, R. Tibshirani and J. Friedman, “Elements of Statistical Learning Ed. 2”, p592-593, Springer, 2009. |
Python source code: plot_ensemble_oob.py
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from collections import OrderedDict
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier, ExtraTreesClassifier
# Author: Kian Ho <hui.kian.ho@gmail.com>
# Gilles Louppe <g.louppe@gmail.com>
# Andreas Mueller <amueller@ais.uni-bonn.de>
#
# License: BSD 3 Clause
print(__doc__)
RANDOM_STATE = 123
# Generate a binary classification dataset.
X, y = make_classification(n_samples=500, n_features=25,
n_clusters_per_class=1, n_informative=15,
random_state=RANDOM_STATE)
# NOTE: Setting the `warm_start` construction parameter to `True` disables
# support for paralellised ensembles but is necessary for tracking the OOB
# error trajectory during training.
ensemble_clfs = [
("RandomForestClassifier, max_features='sqrt'",
RandomForestClassifier(warm_start=True, oob_score=True,
max_features="sqrt",
random_state=RANDOM_STATE)),
("RandomForestClassifier, max_features='log2'",
RandomForestClassifier(warm_start=True, max_features='log2',
oob_score=True,
random_state=RANDOM_STATE)),
("RandomForestClassifier, max_features=None",
RandomForestClassifier(warm_start=True, max_features=None,
oob_score=True,
random_state=RANDOM_STATE))
]
# Map a classifier name to a list of (<n_estimators>, <error rate>) pairs.
error_rate = OrderedDict((label, []) for label, _ in ensemble_clfs)
# Range of `n_estimators` values to explore.
min_estimators = 15
max_estimators = 175
for label, clf in ensemble_clfs:
for i in range(min_estimators, max_estimators + 1):
clf.set_params(n_estimators=i)
clf.fit(X, y)
# Record the OOB error for each `n_estimators=i` setting.
oob_error = 1 - clf.oob_score_
error_rate[label].append((i, oob_error))
# Generate the "OOB error rate" vs. "n_estimators" plot.
for label, clf_err in error_rate.items():
xs, ys = zip(*clf_err)
plt.plot(xs, ys, label=label)
plt.xlim(min_estimators, max_estimators)
plt.xlabel("n_estimators")
plt.ylabel("OOB error rate")
plt.legend(loc="upper right")
plt.show()
Total running time of the example: 23.25 seconds ( 0 minutes 23.25 seconds)

