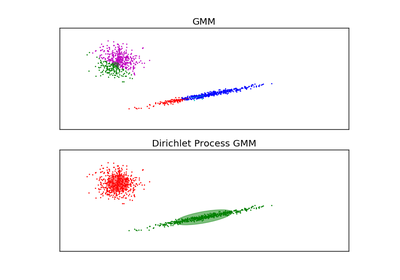
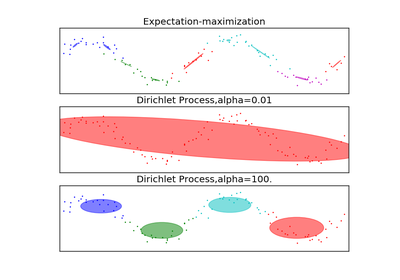
sklearn.mixture.DPGMM¶
-
class
sklearn.mixture.DPGMM(n_components=1, covariance_type='diag', alpha=1.0, random_state=None, thresh=None, tol=0.001, verbose=0, min_covar=None, n_iter=10, params='wmc', init_params='wmc')[源代码]¶ Variational Inference for the Infinite Gaussian Mixture Model.
DPGMM stands for Dirichlet Process Gaussian Mixture Model, and it is an infinite mixture model with the Dirichlet Process as a prior distribution on the number of clusters. In practice the approximate inference algorithm uses a truncated distribution with a fixed maximum number of components, but almost always the number of components actually used depends on the data.
Stick-breaking Representation of a Gaussian mixture model probability distribution. This class allows for easy and efficient inference of an approximate posterior distribution over the parameters of a Gaussian mixture model with a variable number of components (smaller than the truncation parameter n_components).
Initialization is with normally-distributed means and identity covariance, for proper convergence.
Read more in the User Guide.
Parameters: n_components: int, default 1 :
Number of mixture components.
covariance_type: string, default ‘diag’ :
String describing the type of covariance parameters to use. Must be one of ‘spherical’, ‘tied’, ‘diag’, ‘full’.
alpha: float, default 1 :
Real number representing the concentration parameter of the dirichlet process. Intuitively, the Dirichlet Process is as likely to start a new cluster for a point as it is to add that point to a cluster with alpha elements. A higher alpha means more clusters, as the expected number of clusters is
alpha*log(N).tol : float, default 1e-3
Convergence threshold.
n_iter : int, default 10
Maximum number of iterations to perform before convergence.
params : string, default ‘wmc’
Controls which parameters are updated in the training process. Can contain any combination of ‘w’ for weights, ‘m’ for means, and ‘c’ for covars.
init_params : string, default ‘wmc’
Controls which parameters are updated in the initialization process. Can contain any combination of ‘w’ for weights, ‘m’ for means, and ‘c’ for covars. Defaults to ‘wmc’.
verbose : int, default 0
Controls output verbosity.
Attributes: covariance_type : string
String describing the type of covariance parameters used by the DP-GMM. Must be one of ‘spherical’, ‘tied’, ‘diag’, ‘full’.
n_components : int
Number of mixture components.
weights_ : array, shape (n_components,)
Mixing weights for each mixture component.
means_ : array, shape (n_components, n_features)
Mean parameters for each mixture component.
precs_ : array
Precision (inverse covariance) parameters for each mixture component. The shape depends on covariance_type:
(`n_components`, 'n_features') if 'spherical', (`n_features`, `n_features`) if 'tied', (`n_components`, `n_features`) if 'diag', (`n_components`, `n_features`, `n_features`) if 'full'
converged_ : bool
True when convergence was reached in fit(), False otherwise.
参见
Methods
aic(X)Akaike information criterion for the current model fit bic(X)Bayesian information criterion for the current model fit fit(X[, y])Estimate model parameters with the EM algorithm. fit_predict(X[, y])Fit and then predict labels for data. get_params([deep])Get parameters for this estimator. lower_bound(X, z)returns a lower bound on model evidence based on X and membership predict(X)Predict label for data. predict_proba(X)Predict posterior probability of data under each Gaussian in the model. sample([n_samples, random_state])Generate random samples from the model. score(X[, y])Compute the log probability under the model. score_samples(X)Return the likelihood of the data under the model. set_params(**params)Set the parameters of this estimator. -
__init__(n_components=1, covariance_type='diag', alpha=1.0, random_state=None, thresh=None, tol=0.001, verbose=0, min_covar=None, n_iter=10, params='wmc', init_params='wmc')[源代码]¶
-
aic(X)[源代码]¶ Akaike information criterion for the current model fit and the proposed data
Parameters: X : array of shape(n_samples, n_dimensions) Returns: aic: float (the lower the better) :
-
bic(X)[源代码]¶ Bayesian information criterion for the current model fit and the proposed data
Parameters: X : array of shape(n_samples, n_dimensions) Returns: bic: float (the lower the better) :
-
fit(X, y=None)[源代码]¶ Estimate model parameters with the EM algorithm.
A initialization step is performed before entering the expectation-maximization (EM) algorithm. If you want to avoid this step, set the keyword argument init_params to the empty string ‘’ when creating the GMM object. Likewise, if you would like just to do an initialization, set n_iter=0.
Parameters: X : array_like, shape (n, n_features)
List of n_features-dimensional data points. Each row corresponds to a single data point.
Returns: self :
-
fit_predict(X, y=None)[源代码]¶ Fit and then predict labels for data.
Warning: due to the final maximization step in the EM algorithm, with low iterations the prediction may not be 100% accurate
0.17 新版功能: fit_predict method in Gaussian Mixture Model.
Parameters: X : array-like, shape = [n_samples, n_features] Returns: C : array, shape = (n_samples,) component memberships
-
get_params(deep=True)[源代码]¶ Get parameters for this estimator.
Parameters: deep: boolean, optional :
If True, will return the parameters for this estimator and contained subobjects that are estimators.
Returns: params : mapping of string to any
Parameter names mapped to their values.
-
predict(X)[源代码]¶ Predict label for data.
Parameters: X : array-like, shape = [n_samples, n_features] Returns: C : array, shape = (n_samples,) component memberships
-
predict_proba(X)[源代码]¶ Predict posterior probability of data under each Gaussian in the model.
Parameters: X : array-like, shape = [n_samples, n_features]
Returns: responsibilities : array-like, shape = (n_samples, n_components)
Returns the probability of the sample for each Gaussian (state) in the model.
-
sample(n_samples=1, random_state=None)[源代码]¶ Generate random samples from the model.
Parameters: n_samples : int, optional
Number of samples to generate. Defaults to 1.
Returns: X : array_like, shape (n_samples, n_features)
List of samples
-
score(X, y=None)[源代码]¶ Compute the log probability under the model.
Parameters: X : array_like, shape (n_samples, n_features)
List of n_features-dimensional data points. Each row corresponds to a single data point.
Returns: logprob : array_like, shape (n_samples,)
Log probabilities of each data point in X
-
score_samples(X)[源代码]¶ Return the likelihood of the data under the model.
Compute the bound on log probability of X under the model and return the posterior distribution (responsibilities) of each mixture component for each element of X.
This is done by computing the parameters for the mean-field of z for each observation.
Parameters: X : array_like, shape (n_samples, n_features)
List of n_features-dimensional data points. Each row corresponds to a single data point.
Returns: logprob : array_like, shape (n_samples,)
Log probabilities of each data point in X
responsibilities: array_like, shape (n_samples, n_components) :
Posterior probabilities of each mixture component for each observation
-